Krateo Core Provider
The Krateo Core Provider is the foundational component of Krateo Composable Operations (KCO), enabling the management of Helm charts as Kubernetes-native resources.
Key Features
- Dynamic CRD Generation: Automatically creates and manages versioned CRDs from a chart's values.schema.json.
- Schema-Driven Validation: Leverages JSON Schema to enforce strict input validation at the API level, preventing invalid configurations before they are applied.
- Secure Credential Management: Integrates with Kubernetes secrets for seamless authentication against private OCI and Helm repositories.
- Isolated RBAC Policies: Generates and manages fine-grained RBAC policies for each composition, ensuring controllers have the minimum necessary permissions.
- Multi-Version Chart Support: Manages multiple versions of a CompositionDefinition concurrently, allowing for smooth, controlled upgrades and rollbacks.
Security by Design
The Core Provider is built with security as a primary focus:
- Schema-Driven Security: By generating CRDs from values.schema.json, the provider ensures all inputs are validated by the Kubernetes API server, rejecting invalid configurations.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Each deployed composition-dynamic-controller (CDC) is granted only the minimal RBAC permissions required to manage the resources defined within its specific Helm chart.
- Automatic Cleanup: When a CompositionDefinition is deleted, the Core Provider automatically removes the associated CRD, CDC deployment, and all RBAC policies, leaving no orphaned resources.
- Secure Webhooks: Implements mutating and conversion webhooks for advanced schema validation and safe, multi-version API management.
Summary
- Krateo Core Provider
Glossary
- CRD (Custom Resource Definition): A Kubernetes resource that defines custom objects and their schemas, enabling users to extend Kubernetes functionality.
- CompositionDefinition: A CompositionDefinition is a declarative Krateo resource that serves as a master blueprint for a deployable service. It consumes a standard Helm chart as input and uses it to dynamically generate a new, high-level Custom Resource Definition (CRD) in Kubernetes. This process effectively registers the application as a new API within the cluster. It abstracts underlying Helm complexity, establishing a standardized and reusable template for creating application instances.
- Composition: A Composition is a Custom Resource representing a single, live instance of a service defined by a CompositionDefinition. Its CRD is generated from the
values.schema.jsonfile of the Helm chart associated with the CompositionDefinition. The creation of a Composition resource triggers the installation of the associated Helm chart. Its spec field allows for per-instance configuration overrides, enabling customized deployments from a single, authoritative blueprint. - CDC (Composition Dynamic Controller): A dedicated controller deployed by the Core Provider for each CompositionDefinition. The CDC is responsible for managing the lifecycle (create, update, delete) of Helm releases based on Composition resources.
- Helm Chart: A package of pre-configured Kubernetes resources used to deploy applications.
- OCI Registry: A container registry that supports the Open Container Initiative (OCI) image format, used for storing and distributing Helm charts.
- RBAC Policy: A set of rules that define permissions for accessing Kubernetes resources. Typically composed of roles, role bindings, cluster roles, and cluster role bindings assigned to service accounts.
- values.schema.json: A JSON Schema file included in Helm charts to define and validate the structure of
values.yaml.
Architecture
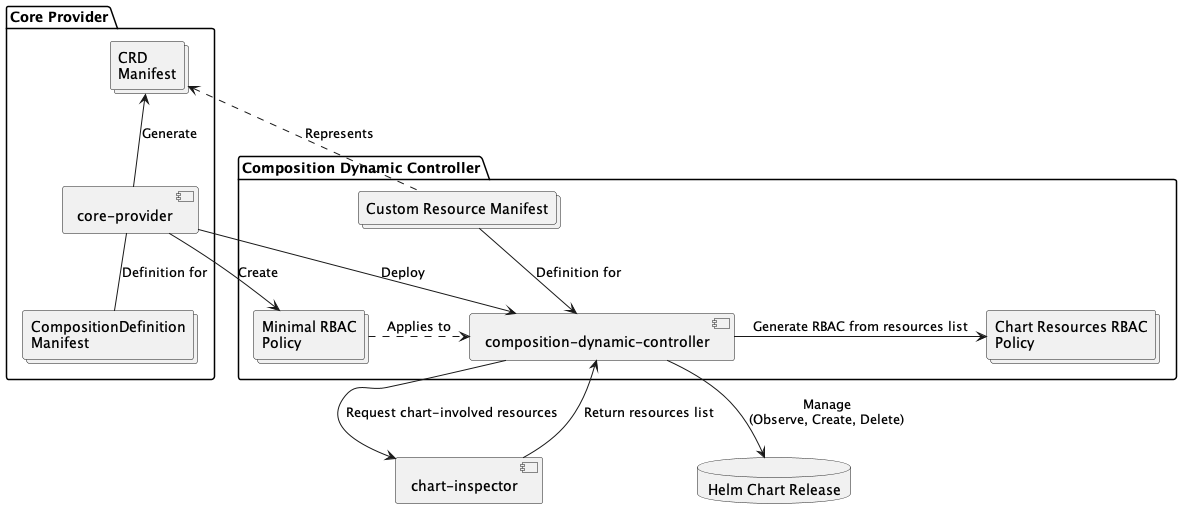
This diagram outlines the high-level architecture and interactions within the Core Provider, responsible for managing CompositionDefinitions and related resources. It illustrates the relationships between key components such as the Core Provider itself, the Composition Dynamic Controller (CDC), the Chart Inspector, and various Kubernetes resources.
The Core Provider generates CRDs, creates RBAC policies, and deploys the CDC. The CDC manages Helm chart releases, requests resource information from the Chart Inspector, and generates RBAC policies based on those resources. The diagram highlights the flow of definitions and resources between these components, showcasing how the Core Provider orchestrates the deployment and management of composed applications within a Kubernetes cluster.
Workflow
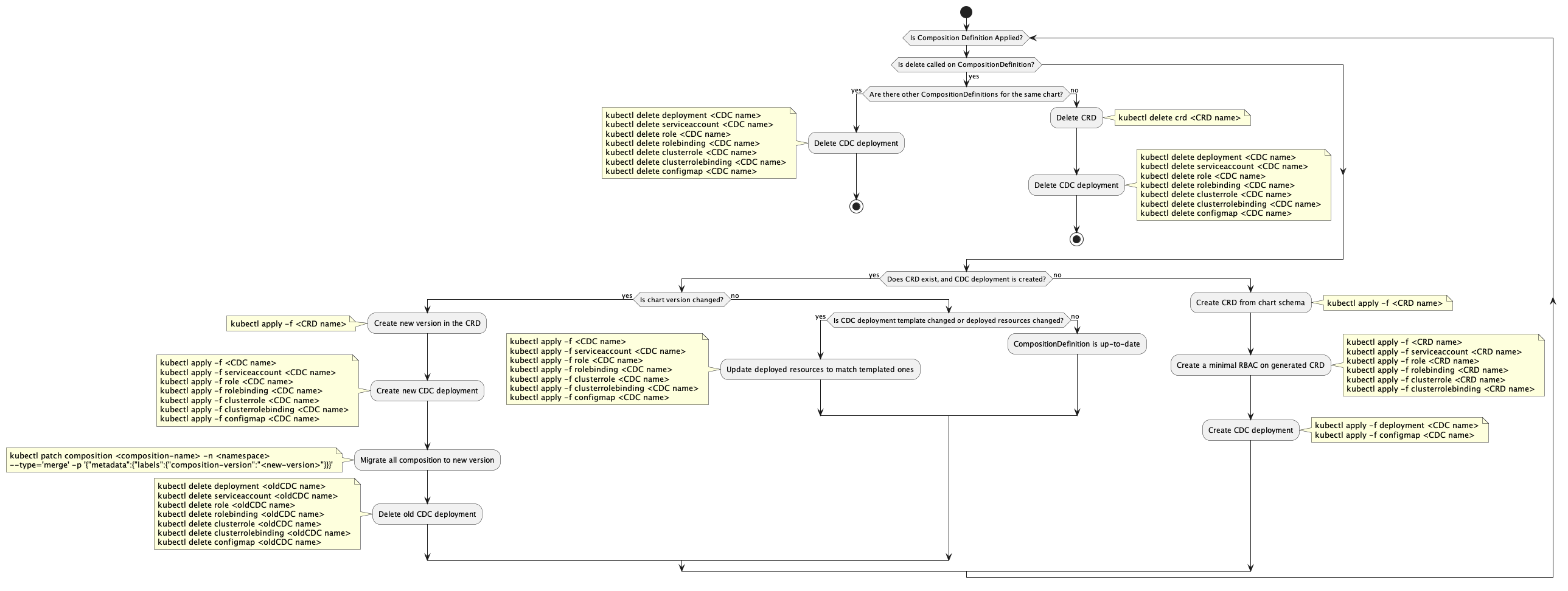
This diagram illustrates the Core Provider's workflow for managing CompositionDefinitions, which define how resources are composed and managed in a Kubernetes environment. It encompasses the lifecycle of Helm releases and associated resources, involving the creation and updating of CRDs (Custom Resource Definitions), RBAC (Role-Based Access Control), and CDC (Composition Dynamic Controller) deployments. These actions are conditional, based on chart versions and the current state of the cluster.
Note: The kubectl commands within the notes serve as illustrative examples of the operations performed by the Core Provider and are not intended for direct user execution. They provide insights into the resource management processes undertaken by the system.
CompositionDefinition specifications and examples
The core-provider is a Kubernetes operator that downloads and manages Helm charts. It checks for the existence of values.schema.json and uses it to generate a Custom Resource Definition (CRD) in Kubernetes, accurately representing the possible values that can be expressed for the installation of the chart.
Kubernetes is designed to validate resource inputs before applying them to the cluster, and the core-provider provides input validation to ensure that incorrect inputs are not accepted.
Defining an Helm Chart compliant with core-provider
A Composition in Krateo is fundamentally a Helm Chart archive (.tgz) that must include a JSON Schema for its values.yaml file. This schema file must be named values.schema.json and is crucial for enabling Krateo's powerful declarative management capabilities.
The values.schema.json file acts as a contract, defining the structure, data types, and validation rules for the configuration values your Helm chart accepts. Krateo's core-provider leverages this schema to:
- Generate Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs): A precise CRD is automatically created in Kubernetes, reflecting the configurable parameters of your Helm chart.
- Enforce Input Validation: Kubernetes can then validate any Custom Resource (CR) instance created from this CRD against the schema, preventing incorrect or malformed configurations from being applied.
- Enable a Robust User Experience: By ensuring only valid configurations are submitted, Krateo provides a more stable and predictable deployment environment. While generic online tools exist for JSON Schema generation, Krateo PlatformOps provides its own official and highly recommended command-line tool: krateoctl. This tool is specifically designed to generate valid and compliant values.schema.json files that are perfectly aligned with Krateo's internal validation mechanisms.
How to use krateoctl to generate values.schema.json
-
Install
krateoctlby following the instructions at Krateoctl Installation Guide. -
Run the following command to get the documentation for the use of the
gen-schemacommand:krateoctl gen-schema --helpBe sure to read the documentation carefully to understand how to use the command effectively and the requirements of the
values.yamlfile. You could also refers to the examples provided in the documentation. -
Generate the
values.schema.jsonfile by executing:krateoctl gen-schema path/to/your/values.yaml -output path/to/output/values.schema.json
Supported Chart Sources
Helm Repository
You can specify a Helm repository URL along with the chart name and version.
Here is an example:
- Helm Repository: An example using the PostgreSQL Helm chart from the Bitnami Helm repository.
OCI Registry
You can specify an OCI registry URL along with the chart name and version.
Here are some examples:
- OCI Registry (specifying repo field): In this example, the
repofield is specified to indicate the chart repository within the OCI registry. - OCI Registry (no repo field specified): In this example, the
repofield is not specified, and the chart is directly referenced from the OCI registry URL.
TGZ Archive
You can provide a direct URL to a .tgz Helm chart archive.
Here is an example:
- TGZ Archive: You can provide a direct URL to a
.tgzHelm chart archive.
Authentication
The core-provider also handles authentication to private OCI registries and Helm repositories. Users can provide their credentials through Kubernetes secrets, and the core-provider will use them to download the necessary chart resources.
OCI Registry
Create the Kubernetes secret:
kubectl create secret generic docker-hub --from-literal=token=your_token -n krateo-system
apiVersion: core.krateo.io/v1alpha1
kind: CompositionDefinition
metadata:
annotations:
"krateo.io/connector-verbose": "true"
name: fireworks-private
namespace: krateo-system
spec:
chart:
url: oci://registry-1.docker.io/yourusername/fireworks-app
version: "0.1.0"
credentials:
username: yourusername
passwordRef:
key: token
name: docker-hub
namespace: krateo-system
GCP Artifact Registry
Follow this guide to create a service account key. You will need to download the .json file containing the key and create the Kubernetes secret from it. Note that the service account should have permissions to download from the Google Artifact Registry.
Now, create a secret from the JSON file containing your service account key:
kubectl create secret generic gcp-sa-secret -n demo \
--from-file=secret-access-credentials=/path/to/file/krateoregistry-3d546566ae4a.json
apiVersion: core.krateo.io/v1alpha1
kind: CompositionDefinition
metadata:
name: fireworks-private
namespace: krateo-system
spec:
chart:
url: oci://europe-west12-docker.pkg.dev/krateoregistry/krateotest/fireworks-app
version: "0.0.1"
credentials:
username: json_key
passwordRef: # reference to a secret
key: secret-access-credentials
name: gcp-sa-secret
namespace: demo
Note: The spec.chart.credentials.username should be set to json_key as explained in this documentation.
Helm Repository
kubectl create secret generic helm-repo --from-literal=token=your_token -n krateo-system
apiVersion: core.krateo.io/v1alpha1
kind: CompositionDefinition
metadata:
annotations:
"krateo.io/connector-verbose": "true"
name: fireworks-private
namespace: krateo-system
spec:
chart:
repo: fireworks-app
url: https://theurltoyourhelmrepo
version: 0.3.0
credentials:
username: yourusername
passwordRef:
key: token
name: helm-repo
namespace: krateo-system
CRD Specification
To view the CRD configuration, visit this link.
Requirements
- Kubernetes 1.30+ or Kubernetes version compatible with Validating Admission Policies
- Helm 3.0+
As of version 0.24.2, the core-provider no longer requires a dependency on Snowplow for resource discovery, as this functionality is now built-in.
How to Install
You can install the core-provider with the following commands:
helm repo add krateo https://charts.krateo.io
helm repo update
helm install krateo-core-provider krateo/core-provider --namespace krateo-system --create-namespace
Examples and Troubleshooting
For practical examples, common issues, and advanced usage patterns, please refer to our Usage Cheatsheet available here.
Environment Variables and Flags
| Name | Description | Default Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
HELM_REGISTRY_CONFIG_PATH | Path to Helm registry configuration file | /tmp | Used for OCI registries |
CORE_PROVIDER_DEBUG | Enables debug logging | false | Use --debug flag |
CORE_PROVIDER_SYNC | Sync period for controller manager | 1h | Duration |
CORE_PROVIDER_POLL_INTERVAL | Poll interval for resource drift checks | 5m | Duration |
CORE_PROVIDER_MAX_RECONCILE_RATE | Maximum reconcile rate per second | 5 | Integer |
CORE_PROVIDER_LEADER_ELECTION | Enables leader election for controller manager | false | Use --leader-election flag |
CORE_PROVIDER_WEBHOOK_SERVICE_NAME | Name of the webhook service | core-provider-webhook-service | String |
CORE_PROVIDER_WEBHOOK_SERVICE_NAMESPACE | Namespace of the webhook service | demo-system | String |
CORE_PROVIDER_MAX_ERROR_RETRY_INTERVAL | Maximum retry interval on errors | 1m | Duration |
CORE_PROVIDER_MIN_ERROR_RETRY_INTERVAL | Minimum retry interval on errors | 1s | Duration |
CORE_PROVIDER_TLS_CERTIFICATE_DURATION | The duration of the TLS certificate. It should be at least 10 minutes and a minimum of 3 times the poll interval. | 24h | Duration |
CORE_PROVIDER_TLS_CERTIFICATE_LEASE_EXPIRATION_MARGIN | The duration of the TLS certificate lease expiration margin. It represents the time before the certificate expires when the lease should be renewed. It must be less than the TLS certificate duration. Consider values of 2/3 or less of the TLS certificate duration. | 16h | Duration |
URL_PLURALS | DEPRECATED from version 0.24.2 - URL to krateo pluraliser service | http://snowplow.krateo-system.svc.cluster.local:8081/api-info/names | String |
Best Practices
- Always Define a Schema: Every Helm chart intended for Krateo should include a comprehensive values.schema.json file. This is the cornerstone of creating robust and predictable compositions.
- Use the paused Annotation: To temporarily halt reconciliation for a composition (e.g., for debugging or manual intervention), apply the
krateo.io/paused: "true"annotation to the CompositionDefinition. - Leverage Multi-Version Support: Manage upgrades and rollbacks smoothly by publishing new chart versions and updating your CompositionDefinition. The Core Provider will handle the deployment of a new controller, allowing old and new instances to coexist until migrated.